Understanding the difference between ultrasound and ultrasonic cavitation is essential for individuals considering their options for body contouring and weight reduction. Both methods utilize sound waves but serve distinct purposes in the realm of aesthetic treatments.
This article will delve into the definitions, mechanisms, and effectiveness of each method, providing clarity for those seeking non-invasive solutions to fat reduction and skin enhancement.
What Is Ultrasonic Cavitation?
Ultrasonic cavitation is a non-invasive aesthetic treatment that aims to reduce localized fat deposits in specific areas of the body. The procedure employs low-frequency sound waves to create bubbles in a liquid medium, which then burst, causing a cavitation effect.
This process helps to destroy fat cells, releasing their contents into the surrounding tissues. The result is a targeted reduction of body fat, making ultrasonic cavitation a popular choice for individuals seeking to sculpt their bodies without invasive methods. Many people opt for this treatment due to its minimal side effects and quick recovery time.
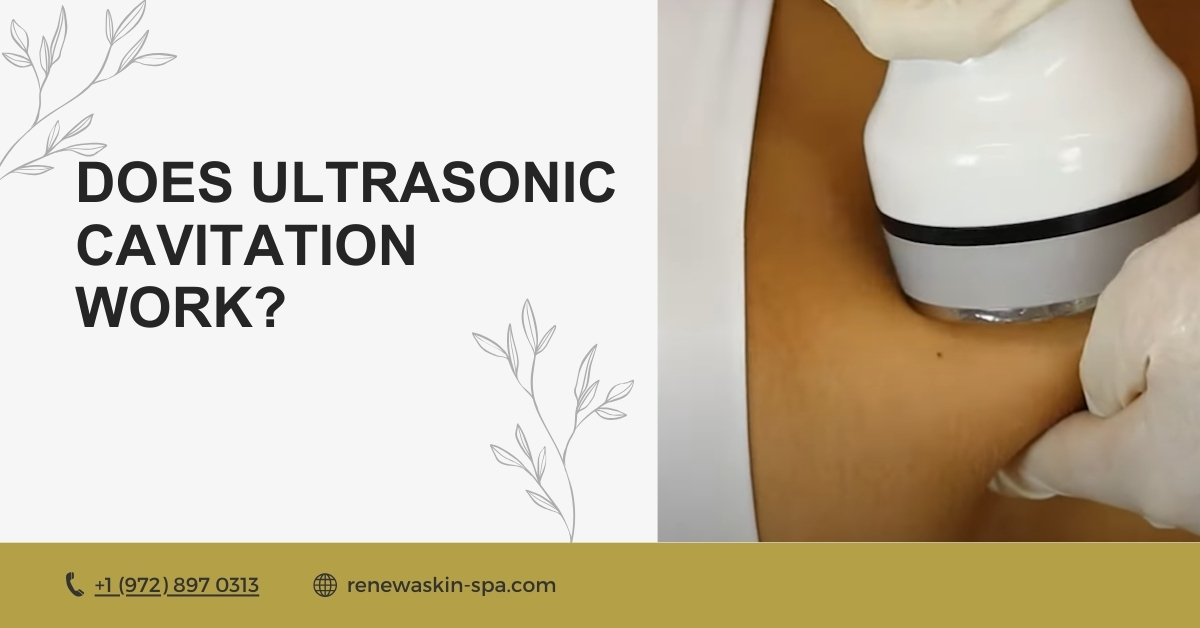
How does Ultrasonic Cavitation Work?
The ultrasonic cavitation procedure works by using high-frequency sound waves that penetrate the skin and target fat cells. When these sound waves reach a specific frequency, they create low-pressure bubbles in the liquid surrounding the fat cells.
As these bubbles expand and collapse, they generate a powerful effect that breaks down fat deposits. This process not only destroys the fat cells but also stimulates the lymphatic system, helping the body eliminate the released fat through natural metabolic processes. Consequently, individuals often notice a reduction in fatty areas following a series of sessions.
How does Ultrasound Work?
Ultrasound, unlike ultrasonic cavitation, is primarily a diagnostic tool that uses high-frequency sound waves to visualize internal body structures. This method is commonly applied in medical settings to assess the condition of organs and tissues.
When ultrasound waves are transmitted into the body, they reflect off different tissues, creating images that can help healthcare professionals make informed decisions about treatment. Although ultrasound does not directly target fat cells, it plays a crucial role in evaluating health conditions and monitoring the body’s response to various treatments.
Does Ultrasonic Cavitation Work?
Ultrasonic cavitation can indeed be effective for individuals aiming to reduce localized fat and improve body contours. However, the success of the treatment often depends on various factors, including the individual’s body condition, diet, and lifestyle choices.
While many people experience visible results after several sessions, it is essential to maintain a healthy diet and incorporate exercise to optimize the effects. The procedure is not a weight-loss solution but rather a method to target specific areas of stubborn fat, making it important for individuals to set realistic expectations.
How Many Treatments Do I Need? How Often Should I be Treated to See Results?
The number of ultrasonic cavitation treatments needed can vary significantly from one individual to another. Generally, a series of six to twelve sessions is recommended to achieve noticeable results, with each session spaced one to two weeks apart.
This frequency allows the body to process and eliminate the broken-down fat effectively. For optimal results, individuals should combine the treatment with a healthy diet and regular exercise. Consulting with a trained professional can help determine the best treatment plan tailored to individual needs and goals.
Cavitation and Ultrasound for Localized Fat Removal

Cavitation and ultrasound serve different but complementary roles in the realm of localized fat removal. Ultrasonic cavitation utilizes low-frequency sound waves to create a cavitation effect that specifically targets and destroys fat cells in certain areas of the body. This non-invasive treatment is designed for individuals looking to sculpt their bodies without undergoing surgical procedures.
In contrast, traditional ultrasound is primarily a diagnostic tool that employs high-frequency sound waves to visualize and assess the condition of tissues and organs but does not directly facilitate fat reduction. Understanding the difference between these two methods is crucial for anyone seeking effective fat loss solutions.
What are Side Effects of Ultrasonic Cavitation?
Cavitation is a non-invasive technology that uses ultrasound at low frequency to target adipose tissue. This treatment is used primarily for slim body shape and is often sought by obese individuals. Although considered standard, other side effects can include mild headaches, nausea, and temporary skin irritation. The head of the device exerts pressure on the human body for up to 12 minutes, promoting metabolism and engaging the liver for processing.
Research indicates that while the treatment is used on adipose tissues, it can not replace a healthy lifestyle. The procedure must be performed in three sessions for optimal results, though high levels of caution are advised. Yes, it is a low-risk procedure, but it is not enough to solely rely on it without dieting and exercising. Consequently, patients should balance expectations with realistic outcomes.
What is Ultrasonic Cavitation After Care?

After undergoing ultrasonic cavitation, proper aftercare is essential to achieve the best results and support the body’s recovery process. Individuals are often advised to maintain hydration by drinking plenty of water, which aids in flushing out the released fat from the body. Engaging in light exercise, such as walking, can also stimulate the lymphatic system and enhance fat elimination.
It’s crucial to avoid high-calorie foods and maintain a healthy diet post-treatment to optimize results. Additionally, practitioners may suggest scheduling follow-up sessions and monitoring progress to ensure the treatment is effectively working for the specific areas targeted.
Is Ultrasonic Cavitation a Safe Treatment?
Ultrasonic cavitation is generally regarded as a safe and effective treatment for localized fat reduction. The non-invasive nature of the procedure means that it does not involve surgical risks associated with invasive methods. Most individuals tolerate the treatment well, with minimal side effects, making it a popular option for those seeking body contouring solutions.
However, as with any aesthetic treatment, individual responses may vary. It is essential for potential candidates to consult with qualified professionals who can evaluate their health condition and determine if they are suitable for the treatment. This ensures a safe experience with optimal results.
Pros and Cons of Using Non-Invasive Methods of Fat Reduction
Non-invasive methods of fat reduction, such as ultrasonic cavitation, come with a mix of advantages and disadvantages. On the positive side, these treatments offer minimal downtime, allowing individuals to resume their daily activities almost immediately. They also target specific areas of fat, making them effective for localized fat deposits.
However, a significant drawback is that these methods are not designed for substantial weight loss, and results can vary based on individual health conditions and lifestyle choices. To maximize the benefits, individuals should commit to a healthy diet and regular exercise, as the success of the treatment can depend heavily on maintaining a balanced lifestyle.
There are also non-invasive fat reduction methods like ultrasound cavitation and radio frequency offer several advantages, such as reduced recovery time and minimal discomfort. These techniques are appealing due to their ability to target specific areas without surgery.